How to open Microsoft Word documents in Linux
 In
an office or production environment, sharing documents between
different applications and operating systems is a common issue. For
creating, opening, and editing Microsoft Word
Documents in Linux, LibreOffice Writer and AbiWord are robust word
processing applications that can read and write files in Word .doc and .docx formats.
In
an office or production environment, sharing documents between
different applications and operating systems is a common issue. For
creating, opening, and editing Microsoft Word
Documents in Linux, LibreOffice Writer and AbiWord are robust word
processing applications that can read and write files in Word .doc and .docx formats.In this tutorial, we'll look at these four applications and how you can use them. We'll walk through installing them on several of the most popular Linux distributions, including Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, OpenSUSE, CentOS, and Arch Linux, and installing the core Microsoft TrueType fonts on your Linux system.
Quick Links
- LibreOffice
- AbiWord
- Antiword (.doc -> text)
- Docx2txt (.docx -> text)
- Installing Microsoft Fonts
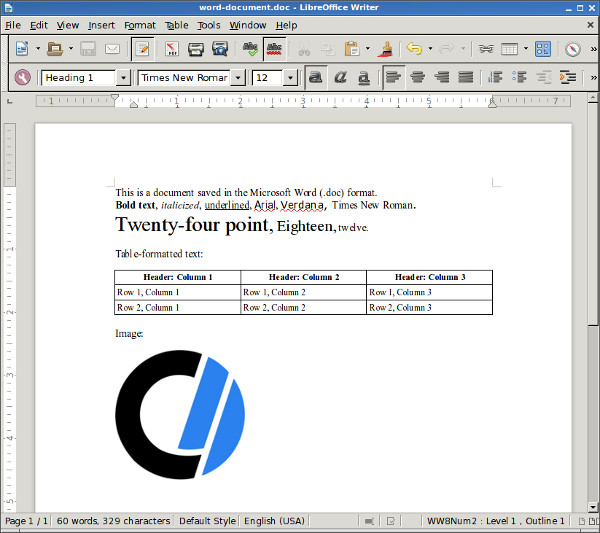
LibreOffice
LibreOffice is a free, open source, actively maintained and frequently updated office productivity suite that is compatible with Microsoft Office
applications, including Microsoft Word. You can save your LibreOffice
Writer documents in .doc or .docx format, and then either opens
correctly in Microsoft Word.
LibreOffice can be installed using your package manager. To install it, open a terminal and use the following command appropriate for your operating system:
Debian 8, Ubuntu 15
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install libreoffice
Fedora 23
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install libreoffice
OpenSUSE 10
sudo zypper refresh && sudo zypper install libreoffice
CentOS 7
sudo yum update && sudo yum install libreoffice
Arch Linux 2016
sudo pacman -Sy libreoffice-fresh
Once LibreOffice is installed, it should appear in the Applications menu of your GUI. You can also run it from a terminal with the command:
libreoffice
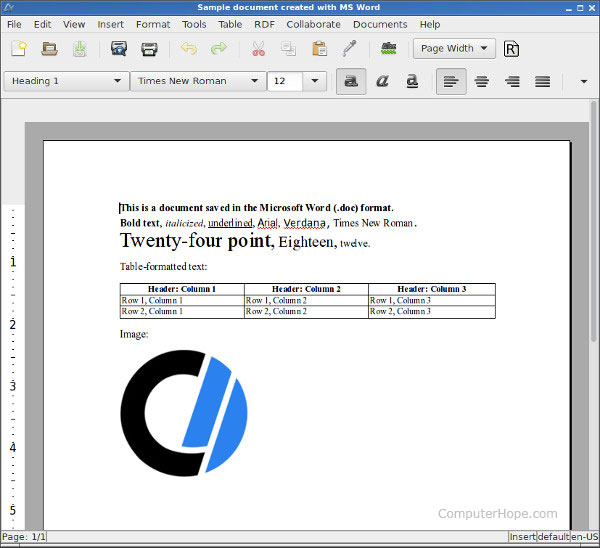
AbiWord
AbiWord is another free and open source word
processor. It has a clean, simple interface and has been in development
for almost twenty years. Like LibreOffice, it can open, edit, and save
Microsoft Word .doc and .docx files. Unlike LibreOffice, Abiword is not a
complete office suite, so it has a smaller footprint and consumes fewer system resources.
Installing AbiWord
Debian 8, Ubuntu 15
sudo apt-get upgrade && sudo apt-get install abiword
Fedora 23
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install abiword
OpenSUSE 10
sudo zypper refresh && sudo zypper install abiword
CentOS 7
sudo yum update && sudo yum install abiword
Arch Linux 2016
pacman -Sy abiword
Antiword
Antiword is a command-line tool that can convert the contents of a .doc file to plain text.
Note: Antiword only converts .doc files. If you need to convert a .docx file, see docx2txt in the next section.
Using antiword
Running "antiword filename" will extract the text from a Word .doc to standard output.

Antiword does a great job of formatting tables. It also has options for including images as PostScript objects and outputting to PDF.
You can redirect the output to a text file:
antiword filename.doc > filename.txt
or, if you want to open it directly in a text editor, you can pipe the text to vim:
antiword filename.doc | vim -
or pico:
antiword filename.doc | pico -
Installing antiword
Debian 8, Ubuntu 15
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install antiword
Fedora 23
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install antiword
OpenSUSE 10
sudo zypper refresh && sudo zypper install antiword
CentOS 7
sudo yum update && sudo yum install antiword
Arch Linux 2016
sudo pacman -Sy antiword
Docx2txt
Docx2txt is a command-line tool that converts .docx files to plain text. (It does not convert .doc files.)
To print the contents of a .docx file to the
terminal screen, or to redirect the output to a file, call docx2txt and
specify a dash as the output filename. In this example, notice the dash
at the end of the command:

To convert a .docx file and output to a text file, use the command form:
docx2txt filename.docx filename.txt
or:
docx2txt filename.docx - > filename.txt
To open the .docx text in vim, use the command form:
docx2txt filename.docx - | vim -
To open it in nano:
docx2txt filename.docx - | nano -
To install doc2txt, follow the instructions for your version of linux below:
Debian 8
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install docx2txt
Ubuntu 15
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install docx2txt
Fedora 23
Fedora's repositories do not offer a package for docx2txt, but you can install it manually:
Download the source from Sourceforge at https://sourceforge.net/projects/docx2txt/. Extract the archive:
tar xzvf docx2txt-1.4.tgz
You need to make sure that perl, unzip and make are installed on your system, so install or upgrade those packages now:
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install perl unzip make
Then, run make as the root user to install:
sudo make
Docx2txt is now installed as docx2txt.sh. For instance, to convert the file word-document.docx to a text file, you can run:
docx2txt.sh word-document.docx
The converted text file will automatically be saved as word-document.txt.
OpenSUSE 10
SUSE repositories do not offer a package for docx2txt, but you can download it from Sourceforge at https://sourceforge.net/projects/docx2txt/. Extract the archive:
tar xzvf docx2txt-1.4.tgz
You need to make sure that perl, unzip and make are installed on your system, so install or upgrade those packages now:
sudo zypper update && sudo zypper install perl unzip make
Then, run make as root to install:
sudo make
Docx2txt is now installed as docx2txt.sh. For instance, to convert the file word-document.docx to a text file, you can run:
docx2txt.sh word-document.docx
The converted text file will automatically be saved as word-document.txt.
CentOS 7
CentOS repositories do not offer a package for docx2txt, but you can download it from Sourceforge at https://sourceforge.net/projects/docx2txt/. Extract the archive:
tar xzvf docx2txt-1.4.tgz
You need to make sure that perl, unzip and make are installed on your system, so install or upgrade those packages now:
sudo yum update && sudo yum install perl unzip make
Then, run make as root to install:
sudo make
Docx2txt is now installed as docx2txt.sh. For instance, to convert the file word-document.docx to a text file, you can run:
docx2txt.sh word-document.docx
The converted text file will automatically be saved as word-document.txt.
Arch Linux 2016
sudo pacman -Sy docx2txt
Installing Microsoft-Compatible Fonts
The core Microsoft fonts are available on Linux,
and you should install them if you are going to be working with
Microsoft Word files — especially if they were created on a Windows
system. The core fonts include:
- Andale Mono
- Arial
- Arial Black
- Calabri
- Cambria
- Comic
- Courier
- Impact
- Times
- Trebuchet
- Verdana
- Webdings
To install them, follow these steps:
Debian 8, Ubuntu 15:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install ttf-mscorefonts-installer
Fedora 23:
Download the msttcore installer RPM package from Sourceforge at this address.
Install packages required for installation:
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install curl cabextract xorg-x11-font-utils fontconfig
Then install the local RPM package:
sudo dnf install msttcore-fonts-installer-2.6-1.noarch.rpm
OpenSUSE 10
Download the msttcore installer RPM package from Sourceforge at this address.
Install packages required for installation:
sudo zypper update && sudo zypper install curl cabextract xorg-x11-font-utils fontconfig
Then install the local RPM package:
sudo zypper install msttcore-fonts-installer-2.6-1.noarch.rpm
CentOS 7:
Download the msttcore installer RPM package from Sourceforge at this address.
Install packages required for installation:
sudo yum update && sudo yum install curl cabextract xorg-x11-font-utils fontconfig
Then install the local RPM package:
sudo yum install msttcore-fonts-installer-2.6-1.noarch.rpm
Arch Linux 2016:
Download the msttcore installer RPM package from Sourceforge at this address.
Install packages required for installation:
pacman -Sy rpmextract x11-font-utils fontconfig
Extract the contents of the local RPM package:
rpmextract.sh msttcore-fonts-installer-2.6-1.noarch.rpm
This command extracts the raw contents of the RPM file. It will create two directories, etc and usr, which correspond to your /etc and /usr directories. The font files themselves are located in usr/share/fonts/msttcore.
Comments
Post a Comment